· Luis Contreras Benito · Mission · 3 min read
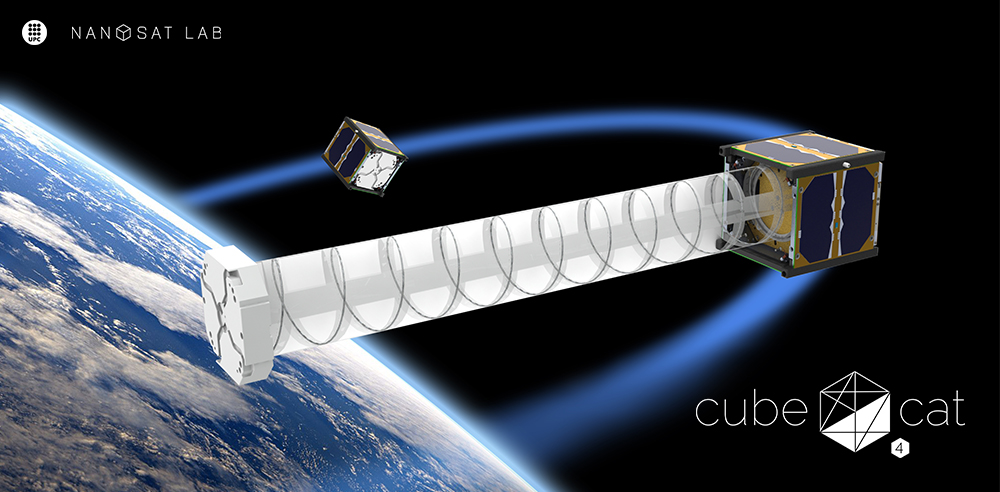
³Cat-4
The fourth satellite in the NanoSat Lab's CubeCat series.
Mission Overview
The ³Cat-4 (read “cube-cat-four”) is the fourth member of UPC’s NanoSat Lab CubeSat series. The mission demonstrates the capabilities of nano-satellites, particularly 1-Unit CubeSats, for Earth Observation (EO) using:
- Global Navigation Satellite System - Reflectometry (GNSS-R)
- L-band microwave radiometry
- Automatic Identification Services (AIS)
Mission Goals
- Educational: Developed by graduate and undergraduate students, who conducted subsystem design, testing, and validation as part of capstone projects or theses.
- Technology Demonstration: Features the Flexible Microwave Payload (FMPL-1), integrating three EO instruments into one subsystem. It also demonstrates payload antenna deployment feasibility.
- Scientific Experiments:
- Assess GNSS-R sensitivity at L1 and L2 frequency bands.
- Analyze ionospheric correction impacts on signal delays.
- Evaluate GNSS-R applications for soil moisture and vegetation biomass measurements, especially over forests.
- Investigate RFI detection and mitigation for digital radiometers.
- Create RFI maps at L1, L2, and the 1400-1427 MHz protected band.
- Validate AIS receiver designs for space applications.
Program Participation
The ³Cat-4 mission is part of the ESA Academy’s “Fly Your Satellite!” program (second edition).
Technical Specifications
| Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Spacecraft Class | 1-Unit CubeSat |
| Total Mass | 1.3 kg |
| Stowed Dimensions | 100 mm x 100 mm x 113.5 mm |
| Deployed Dimensions | 100 mm x 100 mm x 595.75 mm |
| Mission Status | Phase D2: System Verification |
| Expected Launch Date | Summer 2024 |
| Launcher Details | Maiden Flight of Ariane 6 |
| Sponsor | European Space Agency (ESA) |

CubeSat Architecture
The ³Cat-4 consists of the following subsystems:
- Zenith Antenna and Deployment Subsystem (ZADS): Deployable monopole antenna system with VHF and UHF antennas.
- Communications Subsystem (COMMS): Manages satellite-ground station communications.
- Attitude and Orbit Control Subsystem (AOCS): Ensures spacecraft orientation determination and control.
- On Board Computer (OBC): Provides processing, data handling, and subsystem interfacing.
- Electrical Power Subsystem (EPS): Collects and distributes electrical power to subsystems.
- Flexible Microwave Payload (FMPL-1): Combines GNSS-R, L-band radiometer, and AIS receiver experiments.
- Nadir Antenna and Deployment Subsystem (NADS): Deploys L-band antenna and generates gravity gradient stabilization.
- Solar Panels (SP): Collect solar energy and determine orientation via Sun sensors.
- Interface Board: Connects the satellite to ground-based PCs for programming and debugging.
Key Payload: Flexible Microwave Payload (FMPL-1)
The FMPL-1 integrates three instruments using Software Defined Radio (SDR):
- Automatic Identification Service (AIS) Receiver: Tracks vessels in remote areas lacking infrastructure.
- L-Band Microwave Radiometer: Studies soil moisture and vegetation biomass.
- GNSS-Reflectometer (GNSS-R): Measures surface roughness and ice coverage.
On-Board Data Processing
The FMPL-1 employs a System On-Module (SOM) for raw measurement formatting and features RF reception chains to maximize signal quality.
Subsystem Highlights
On-Board Computer (OBC)
- Model: NanoMind A3200 from GomSpace
- Specifications: Atmel AT32UC3C MCU (8-64 MHz), 128 MB NOR flash
- Software: FreeRTOS for task management and real-time operations
- Functions: Energy management, task scheduling, communication, and sensor monitoring
Electrical Power Subsystem (EPS)
- Model: Nanopower P31u by GomSpace
- Components: Two 2600 mAh Li-Ion batteries, AzurSpace 3G30A solar cells (30% efficiency)
- Power Management: Adaptive DC/DC converters and microcontroller-driven distribution
Communication Subsystem
- Frequency: UHF band (437.35 MHz)
- Components: TI CC1101 transceiver, RF amplifier, and LNA
- Antenna: Deployable monopole with omnidirectional pattern
Attitude and Orbit Control Subsystem (AOCS)
- Sensors: Sun sensors, magnetometer, and gyroscope
- Control Algorithms: B-dot detumbling and PID-based nadir pointing
- Actuators: Three magnetorquers generating 0.2 Am²
How to Receive Telemetry
Interested collaborators can decode telemetry signals from ³Cat-4. Details will be available closer to the launch date, including recommended setup and signal specifications.